In order to establish the current status of a building and the possibilities for reducing energy consumption, an energy audit of the building is carried out. Energy audit and energy certification of buildings are carried out by certified persons authorised by the Ministry of Physical Planning, Construction and State Assets pursuant to the Ordinance on conditions and criteria for persons performing energy audits of buildings and energy certification of buildings (OG 81/12, 64/13). The Register of natural and legal persons authorised for energy audits and energy certification of buildings is published on the website of the Ministry of Physical Planning, Construction and State Assets.
An energy audit of a building has to be carried out in accordance with the Ordinance on energy audit and energy certification (OG 48/14, 150/14) and the Ordinance amending this Ordinance (OG 90/2020).
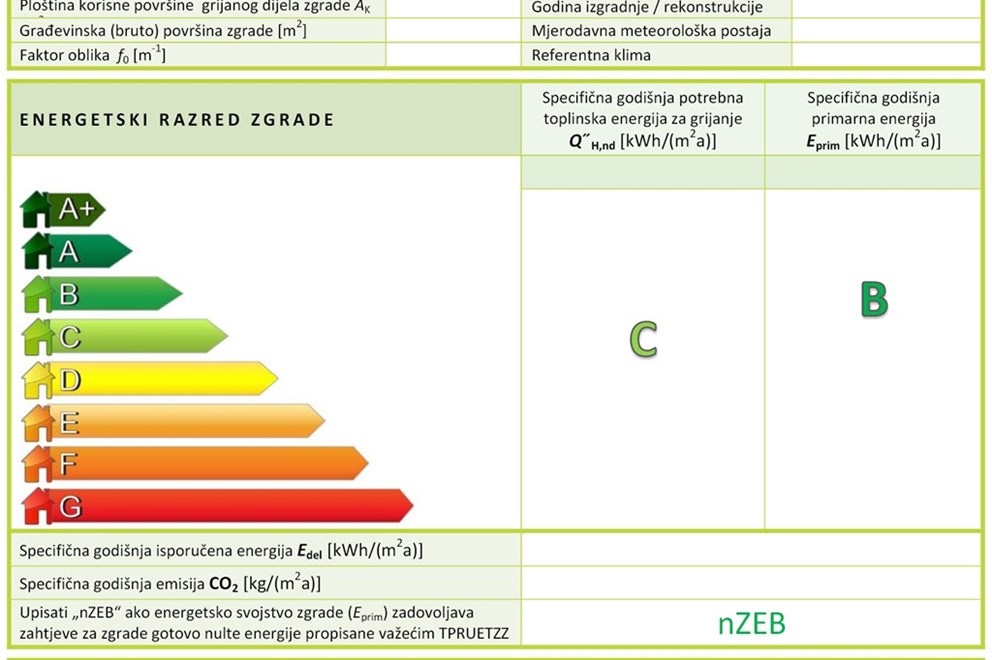
The result of an energy audit is the energy performance certificate – the document describing the building’s energy performance, and it is drawn up by an energy auditor. The document is valid for 10 years from the date of issue and it contains general information about the building, energy class of the building, certificate validity period, the information about the person who issued and drew up the energy performance certificate, information about the persons who took part in the preparation of the energy certificate, energy certificate rating, data about the building’s thermal and technical systems, energy requirements, information about the use of RES, proposals for measures, detailed information and explanation of the energy performance certificate.
Energy class is expressed for the reference climate data set and it is an indicator of:
- specific annual heating energy requirements for the reference climate data and space use and technical systems operation regime defined by an algorithm,
- specific annual primary energy for the reference climate data and space use and technical systems operation regime defined by an algorithm, which in residential buildings includes heating energy, hot domestic water and ventilation/AC (ventilation/AC is taken into account if installed and only in terms of heating), and in commercial buildings it includes the energy for lighting and the energy for those thermal-technical systems indicated in the Methodology in Table 5.18 (Defined technical systems for the calculation of the primary energy for the reference climate data for individual types of buildings) for certain types of commercial buildings (office building, schools, hospitals, hotels and restaurants, sports halls, commercial buildings, other non-residential buildings);
Residential and non-residential buildings are categorised in eight energy classes according to the energy rating scale from A+ to G, where the A+ is the most energy efficient, and G is the least energy efficient class.
More information about energy audits and certification is available on the website of the Ministry of Construction and Physical Planning , or the Ministry’s telephone number 01/3782 444.
Construction regulations that are currently in force in the Republic of Croatia lay down that all new buildings for which the request for a building permit is submitted after 31 December 2019 have to meet the requirements for nZEB – nearly zero-energy buildings. It is desirable to design the buildings in such a way to ensure as low as possible energy requirements. There are no universal solutions to achieving the nZEB standard. Every building has to be considered in detail and efforts have to be made to define the optimum energy concept, i.e. to balance the thickness of thermal insulation and thermal-technical systems, with mandatory use of RES systems. More information is available in the nZEB Guidelines.
*Example of energy class of a building